Last update images today Ancient Greece: A Land Shaped By Geography
Ancient Greece: A Land Shaped by Geography
This week, let's delve into the fascinating physical map of ancient Greece and explore how its unique features shaped its civilization. Forget fleeting trends; we're diving into a timeless topic that remains relevant for history buffs, students, and anyone curious about the cradle of Western civilization.
Introduction: The Rugged Beauty of Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece wasn't just a collection of city-states; it was a land sculpted by mountains, islands, and a vibrant coastline. The physical map of ancient Greece profoundly influenced its development, shaping its economy, politics, and culture. Understanding this geography is key to understanding the rise and fall of this incredible civilization. We'll explore the key geographical features and their impact.
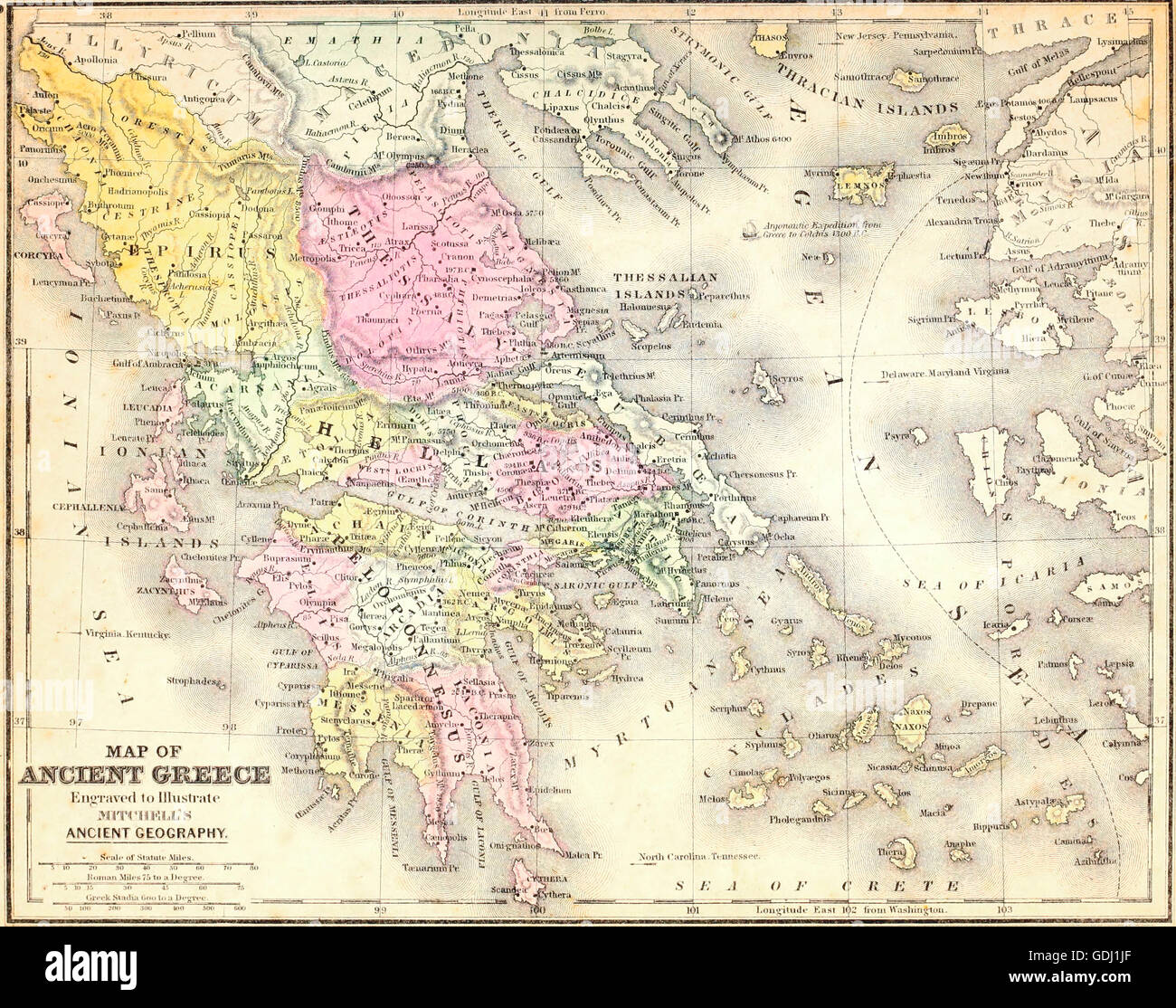
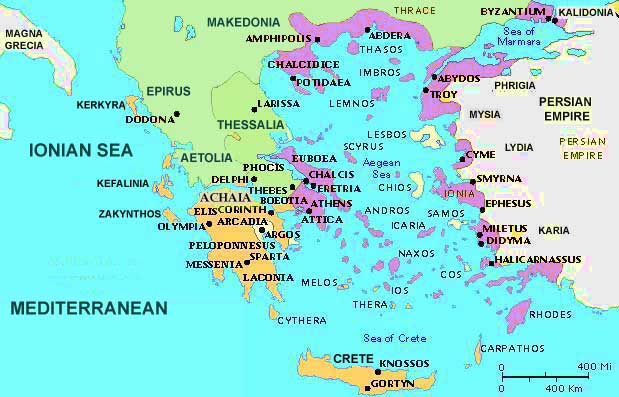
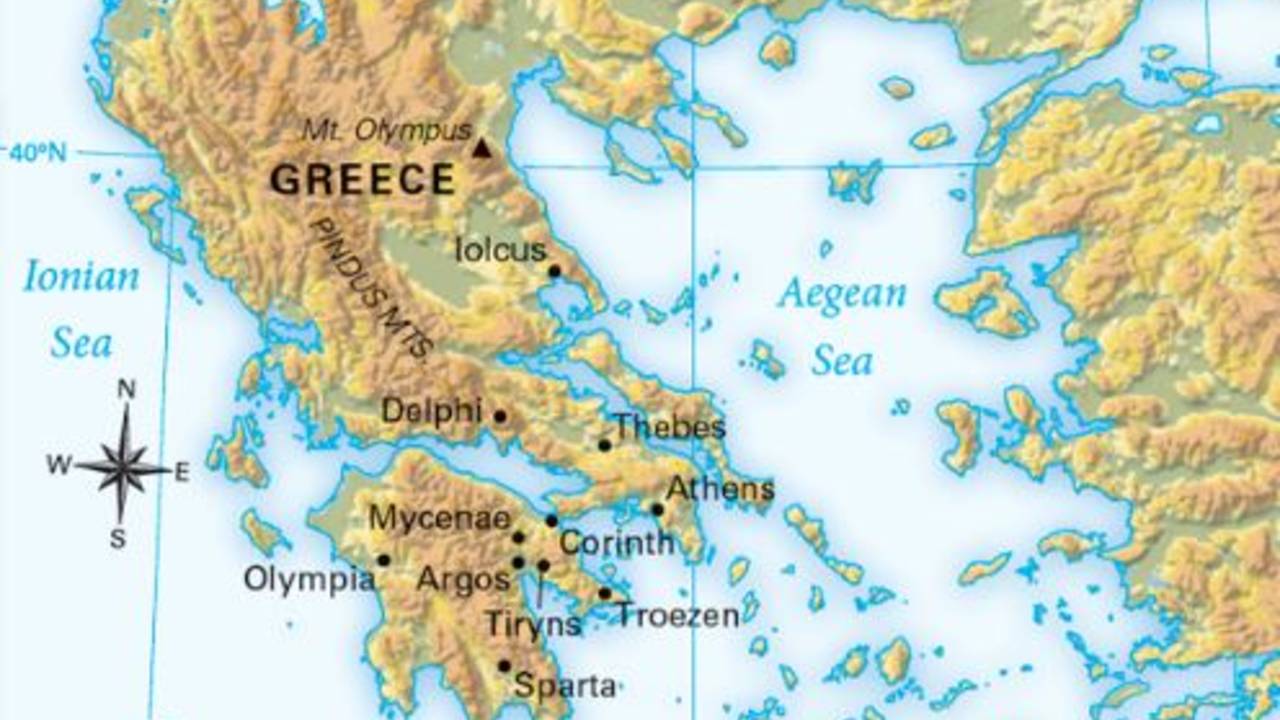
1. The Mountains of Ancient Greece: Natural Barriers and Independent City-States
Physical Map of Ancient Greece: Mountains
[Image of a mountain range in Greece with the caption: "The Pindus Mountains, a major barrier in ancient Greece."] ALT Text: Pindus Mountains in Greece
The Greek landscape was dominated by rugged mountains, particularly the Pindus range, which ran down the spine of the mainland. These mountains presented significant challenges.
- Isolation: The mountains created natural barriers, dividing the land into isolated valleys and plains. This isolation hindered unification and fostered the development of independent city-states (poleis) like Athens, Sparta, and Corinth. Communication and travel were difficult, reinforcing local identities.
- Limited Agriculture: Fertile land was scarce, restricted to coastal plains and river valleys. This scarcity led to competition for resources and the need for trade. Agriculture was often subsistence-based, focusing on crops like olives, grapes, and barley.
- Defense: The mountainous terrain offered natural defenses against invasion. City-states could fortify strategic passes and mountaintops, making conquest difficult. Sparta, in particular, used its mountainous location to its advantage, creating a formidable military society.
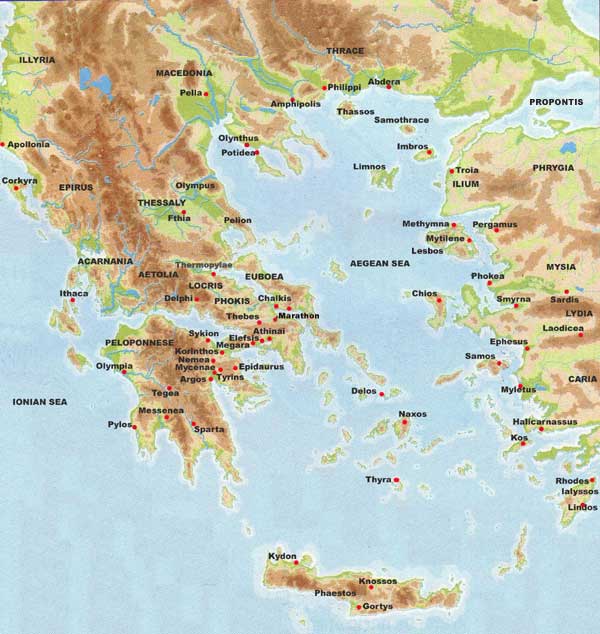
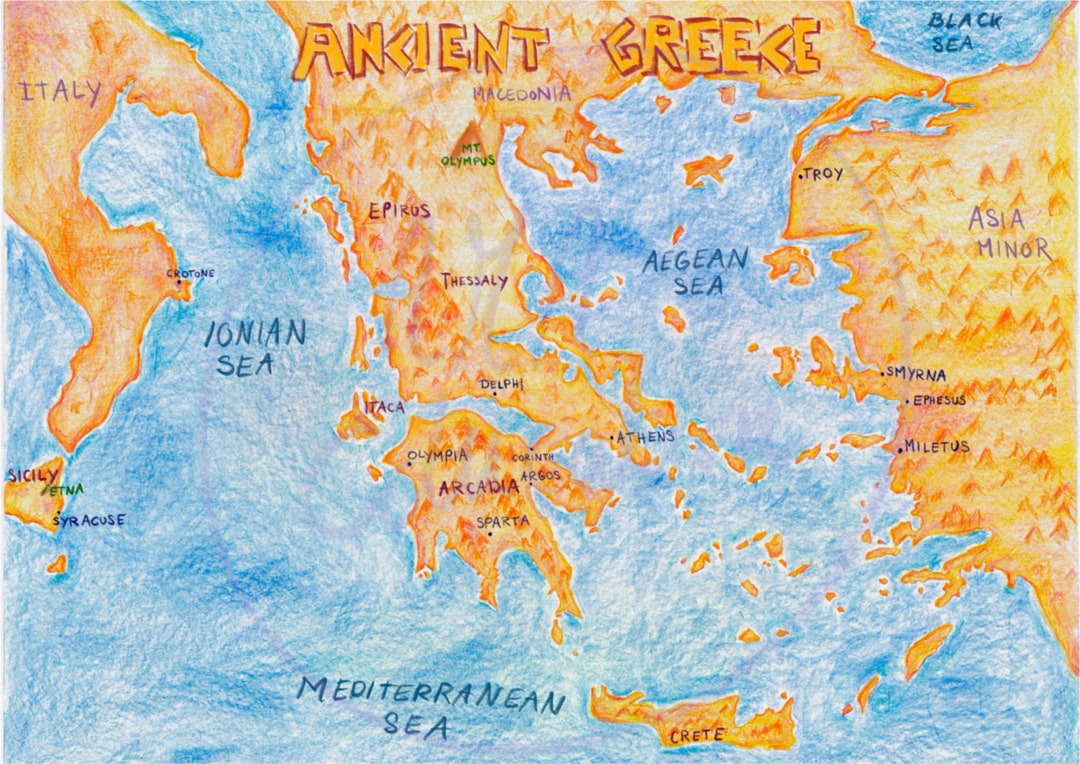
2. The Coastline and Islands of Ancient Greece: A Maritime Culture
Physical Map of Ancient Greece: Coastline and Islands
[Image of the Aegean Sea with Greek islands scattered throughout, with the caption "The Aegean Sea, a crucial waterway for ancient Greek trade and colonization."] ALT Text: Greek Islands in the Aegean Sea
The extensive coastline and numerous islands of ancient Greece were just as crucial as the mountains.
- Seafaring Tradition: With limited agricultural land, the Greeks turned to the sea for sustenance and trade. They became skilled sailors and navigators, establishing trade routes throughout the Mediterranean.
- Colonization: Overpopulation and resource scarcity drove the Greeks to establish colonies throughout the Mediterranean and Black Sea regions. These colonies spread Greek culture and influence far beyond the mainland.
- Naval Power: Control of the seas was essential for trade and defense. City-states like Athens built powerful navies, becoming major maritime powers. The Battle of Salamis, where the Greek fleet defeated the Persian navy, is a prime example of the importance of naval power.
- Island Life: Islands like Crete, Rhodes, and Delos developed distinct cultures and economies. Crete, for example, was home to the Minoan civilization, which predated the Mycenaean Greeks.
3. The Climate of Ancient Greece: Shaping Daily Life
Physical Map of Ancient Greece: Climate
[Image showing a map of Greece with climate zones highlighted, with the caption "The Mediterranean climate of ancient Greece, characterized by mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers."] ALT Text: Climate Map of Greece
The Mediterranean climate of ancient Greece--characterized by mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers--played a significant role in shaping daily life.
- Agriculture: The climate was well-suited for growing olives, grapes, and grains, which formed the basis of the Greek diet.
- Outdoor Lifestyle: The mild climate encouraged outdoor activities, such as athletics, festivals, and public gatherings. The gymnasium, a place for physical training and intellectual discussion, became a central feature of Greek society.
- Clothing and Architecture: The climate influenced clothing styles (light, airy garments) and architectural designs (open-air courtyards, colonnades).
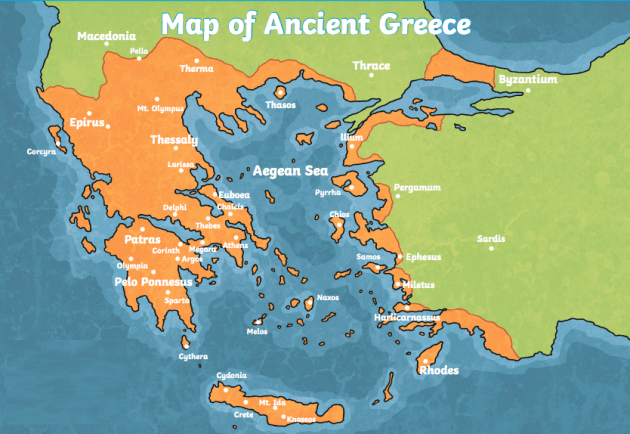
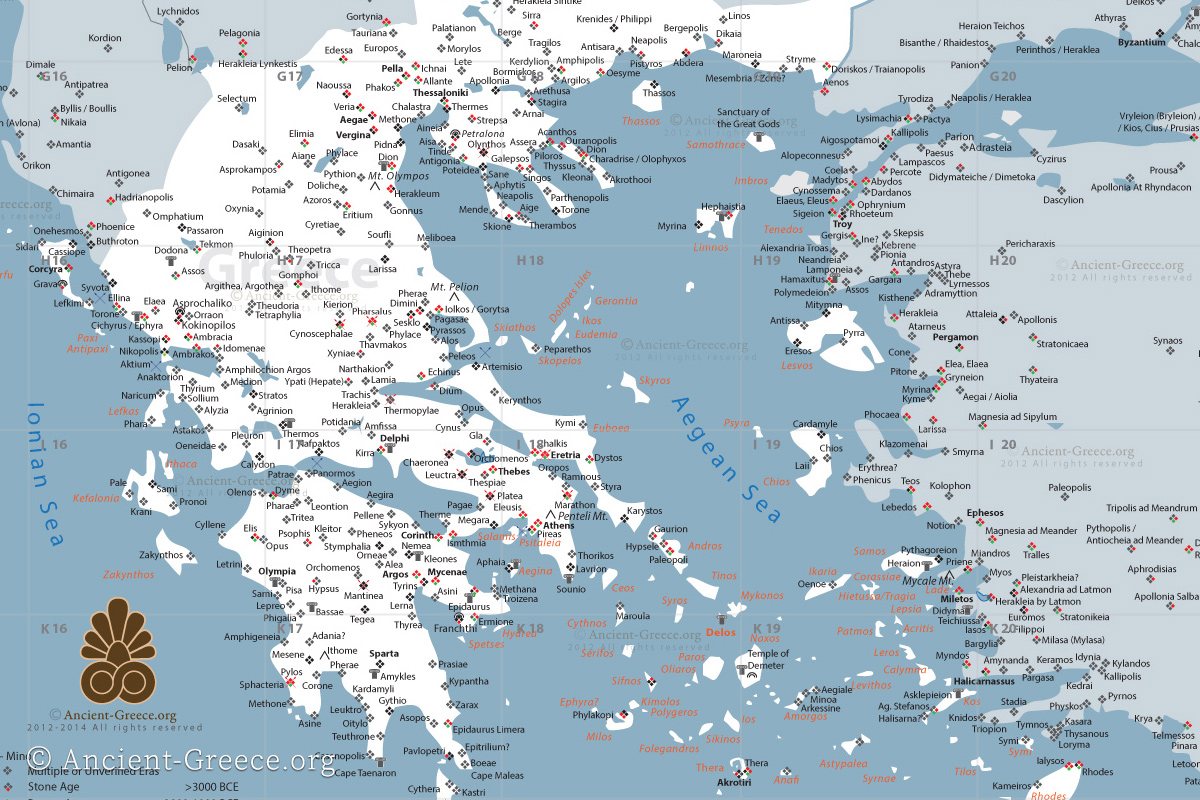
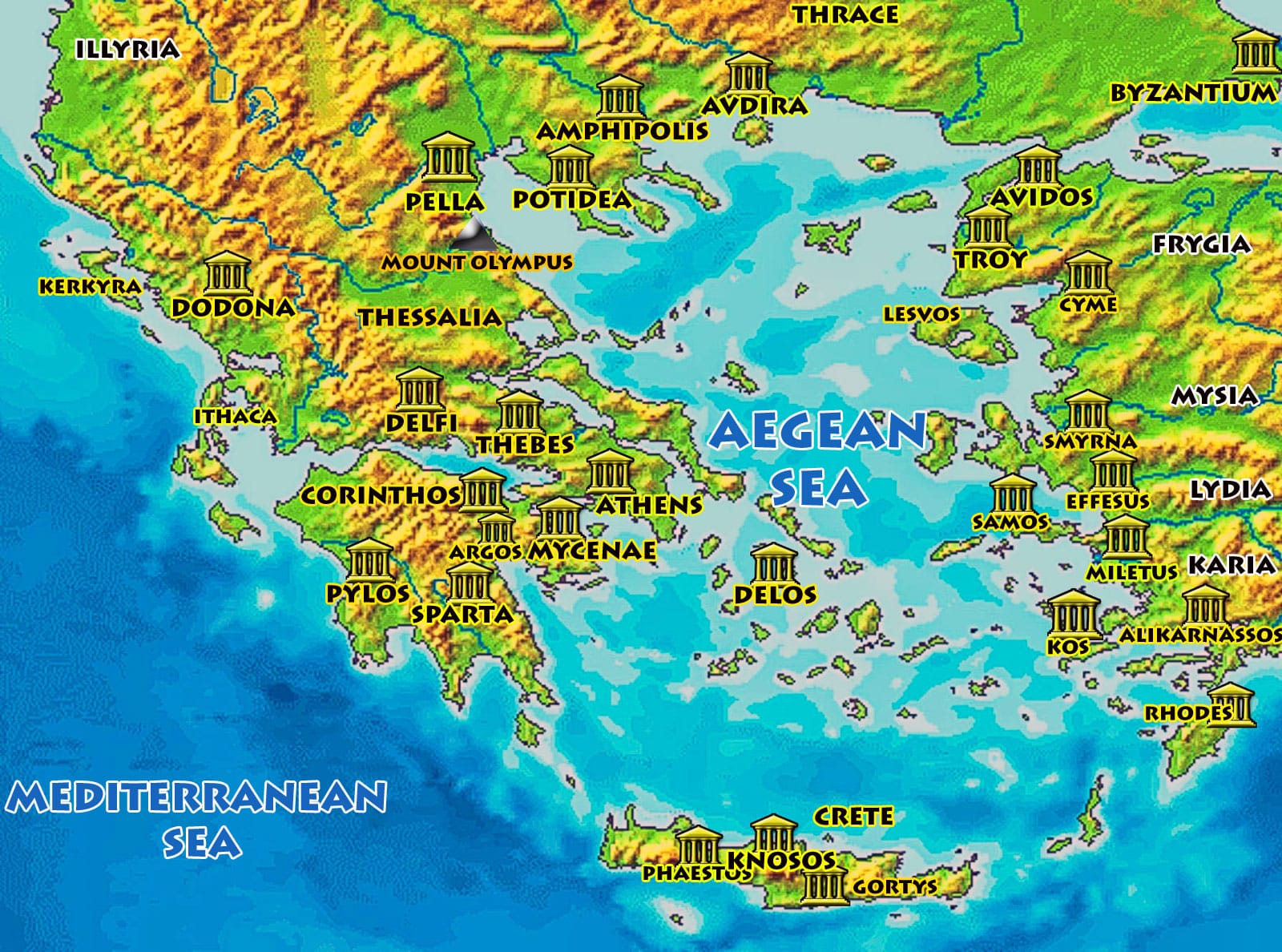
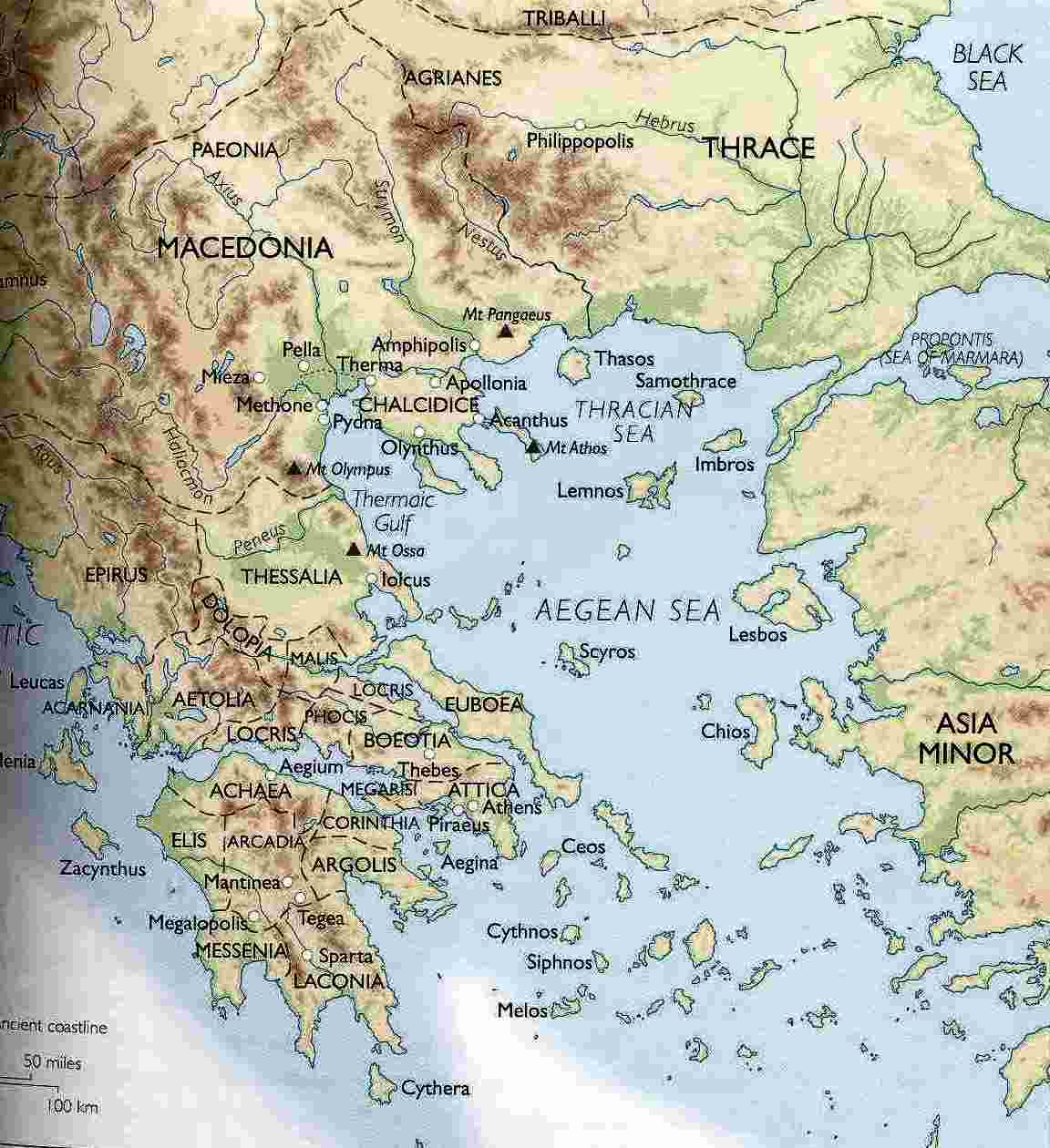
4. Key Regions of Ancient Greece and their Characteristics
Physical Map of Ancient Greece: Key Regions
[Image showing a map of ancient Greece highlighting key regions like Attica, Laconia, Boeotia, and Thessaly, with the caption "Key regions of ancient Greece, each with its unique geographical features and historical significance."] ALT Text: Regions of Ancient Greece Map
- Attica: The region surrounding Athens, known for its fertile plains and access to the sea. This facilitated trade and the development of a powerful navy.
- Laconia: The region surrounding Sparta, characterized by its mountainous terrain and isolation, fostering a militaristic society.
- Boeotia: A fertile plain north of Attica, often contested by Thebes and other city-states.
- Thessaly: A large, fertile plain in northern Greece, known for its horse breeding.
- Peloponnese: The peninsula south of the Isthmus of Corinth, home to Sparta, Argos, and Corinth.
5. Impact on Ancient Greek Culture and Society
The physical map of ancient Greece wasn't just scenery; it was a powerful influence on all aspects of life.
- Political Fragmentation: The mountainous terrain contributed to the development of independent city-states and prevented the unification of Greece under a single ruler (until the rise of Macedon).
- Economic Development: Limited agricultural resources led to a reliance on trade and colonization, making the Greeks skilled sailors and merchants.
- Military Strategies: The mountainous terrain influenced military tactics, favoring defensive strategies and guerrilla warfare. The sea was crucial for naval power and control of trade routes.
- Cultural Identity: The connection to the land and sea shaped Greek mythology, religion, and art. Gods like Poseidon (god of the sea) and Gaia (goddess of the Earth) were central to Greek beliefs.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Geography
The physical map of ancient Greece played a pivotal role in shaping its history, culture, and society. From the isolating mountains to the inviting coastline, the geography of ancient Greece left an indelible mark on this remarkable civilization. Understanding this interplay between land and people is crucial to appreciating the enduring legacy of ancient Greece.
Keywords: Ancient Greece, Physical Map, Geography, Mountains, Coastline, Islands, Climate, City-States, Athens, Sparta, Peloponnese, Mediterranean, Colonization, Trade, History
Summary Question and Answer:
Q: How did the mountains of Greece influence its development? A: The mountains created natural barriers, leading to the development of independent city-states, limited agricultural land, and provided natural defenses.

















Accurate Map Of Ancient Greece Il 1080xN.3781815229 E4os Ancient Greece S Geographical Impact Lesson And Essay Assessment By Original 862259 1 Ancient Greece Map Atra 1ebed15d846a6d7d410c1eb6ddc78d7e Ancient Greece Map Printable 90920be063c403e2e436020e696ac970 Physical Map Of Ancient Greece Map Of Massachusetts GreecePhysicalMap Map Of Ancient Greece Map Of Ancient Greece 1 1 1 Alps Map Of Ancient Greece Greece Map Features Locator
Ancient Greek City States A Comprehensive Summary Crunch Learning Ancient Greece Map 1024x699 Map Of Ancient Greece Ancient Greece Ancient Greece Map Ancient 892deab007a3ee8d85151e5d3236622f The Geography Of Ancient Greece Mr Galloway S Webpage Greece Physical Map Ancient Greece Brief History Map Of Archaic Greece English Geography In Ancient Greece Physical Map Of Classical Greece Ancient Greece Map With Cities Map Map Of Ancient Greece GDJ1JF Geography Of Ancient Greece Ancient Greece Greece Geography 62352029f45286193eaee8a87c790aeb Download Physical Maps Of Greece Ancient Greece Map Transparent 182 1821588 Physical Maps Of Greece Ancient Greece Map Transparent
Map Of Ancient Greece And Its Major Cities NBKomputer Map Of Ancient Greece Geography Of Ancient Greece The First Encyclopedia Geography Of Ancient Greece Map Of Ancient Greece Display Poster Ancient Greece Map T2 H 5715 Map Of Ancient Greece Display Poster Ver 5 Geographical Regions Of The Ancient Greece Vrogue Co PFyXUnRiubnv7vDVGlAC Pasted Image 0 9 Alps Map Of Ancient Greece Greece Map Square Alps Map Of Ancient Greece Greece Hd Map Regions Of Ancient Greece Ancient Greece Facts Com Regions Of Ancient Greece
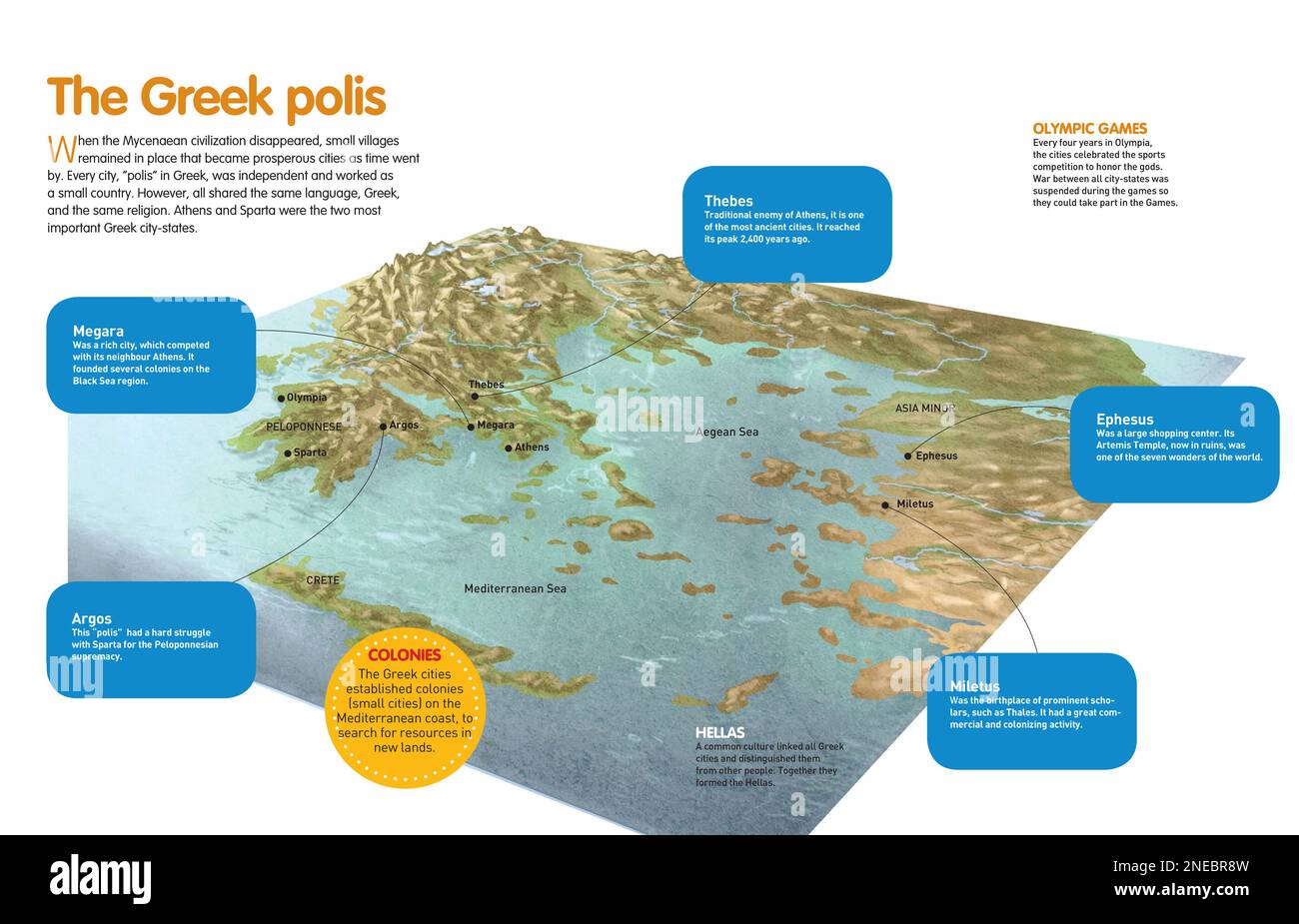
Geography Of Greece Facts At Nicholas Ramsey Blog 08fde0b A867 Caa7 403b F1e2ed7834e 2575f9c8 Bfc9 46f6 8707 13cd0eedf753 Maps Ancient Greece Org Greece Map Featured 1200x800 1 Maps Of Ancient Greece Map Of Ancient Greece 1 1 Free Printable Map Of Ancient Greece 3a67800be4bdff82f3ff2f270b480fca Infographic Of The Geographical Site Where The Greek Polis Developed Infographic Of The Geographical Site Where The Greek Polis Developed Cities Of Ancient Greece And Location Of The Most Important Ones Quarkxpress Qxp Adobe Indesign Indd 4960x3188 2NEBR8W
Map Of Ancient Athens Greece Stock Vector Vector Map Of The Ancient Greece 1647230491 Elevation Map Of Ancient Greece United States Map XLOAeOW1S7Sg3vIdKa5J Ancient Greece Geography Ancient Greece Geography Ancient Greece Facts Com Ancient Greece Geography And Antique Maps 768x905

